Abstract
Telomeres are DNA repeats at the ends of the chromosomes that are important for maintaining genomic integrity by preventing erosion of the ends. Short telomeres in CLL have previously been shown to be associated with inferior prognosis however its prognostic relevance in chlorambucil based treatment has not been studied. Here, we evaluated associations and prognostic relevance of telomere length in CLL treated with chlorambucil (CLB), CLB+Rituximab(CLB+R) and CLB+Obinutuzumab (GA-101) (CLB+G) in the international, multicenter, randomized CLL11 trial. Telomere length was analyzed using a Q-PCR based method on a representative cohort of 700 patients (89.6%) with available DNA from CD19 enriched or unsorted PBMCs. The method was validated using terminal restriction fragment length analysis (TRF; R2=0.915).
Telomere length in CLL11 patients was highly variable (2.2kb to 28.6kb) with a median telomere length of 4.2kb. Telomere length associations were studied by dichotomizing into short (≤median) and long (>median) telomere subgroups. Among the clinical parameters, telomere length showed no association with age, ECOG status, presence of B symptoms, CIRS score, and serum b2-microglobulin (b2-MG). However, short telomeres were significantly associated with male sex (P=0.010), Binet stage (P=0.001), serum thymidine kinase level (s-TK; P<0.001), WBC count (P<0.001), and the CLL-IPI risk group (P<0.001). Among the genetic characteristics, short telomeres were found to be significantly associated with unmutated IGHV (P<0.001), presence of 17p- or 11q- (P<0.001) and TP53 (P=0.029), SF3B1 (P<0.001) and NOTCH1 (P=0.005) mutations.
Regarding outcome, telomere length was associated with response to therapy in the CLB+R (P=0.001) and CLB+G (P=0.023) treatment arms, while no significant association was observed for the CLB group (P=0.275). Moreover, short telomeres were significantly associated with positive MRD in bone marrow (89.8% vs. 72.9%; P=0.018) and as a trend in peripheral blood (70.2% vs. 58.2%; P=0.068) for CLB+G treatment.
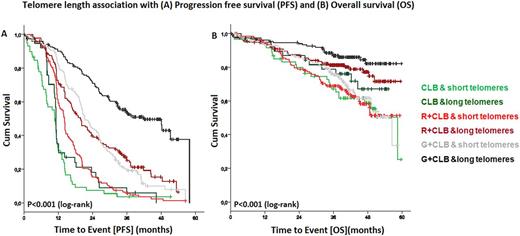
At a median observation time of 41.6 months, there were 534 (76.3%) events for progression free survival (PFS) and 195 events (27.9%) for overall survival (OS). Telomere length showed a statistically significant association with PFS (P<0.001) and OS (P<0.001) with short telomeres being associated with poor outcome. However, the difference in PFS was more evident in patients treated with CLB+R (14.1 vs. 19.8 months; P<0.001) and CLB+G (21.2 vs. 42 months; P<0.001) while patients treated with CLB alone had short PFS irrespective of telomere length (10.8 vs. 11.1 months; P=0.226). Similarly, for OS, the poor prognostic impact of short telomere was apparent in the CLB+R (P=0.004) and CLB+G (P<0.001) and not for CLB treatment (P=0.218).
Multivariable analysis to identify independent prognostic factors was performed including variables significantly associated with PFS in univariate analysis such as treatment arms, Binet stage, b2-MG, s-TK, WBC count, presence of 17p- and/or TP53 mutation, 11q-, mutation status of IGHV and NOTCH1 and telomere length. Short telomeres (HR 1.307; 95%CI 1.054-1.622; P=0.015) along with the treatment arms CLB+R (P<0.001) and CLB+G (P<0.001), Binet A stage (P=0.012), WBC count (P=0.001), IGHV (P<0.001), presence of 17p- and/or TP53 mutation (P<0.001) and 11q- (P=0.041) were found to be independent prognostic factors for PFS. Multivariable analysis for OS was performed with treatment arms, age, sex, Binet stage, ECOG, CIRS score, b2-MG, s-TK, presence of 17p- and/or TP53 mutation, 11q-, mutation status of IGHV and NOTCH1 and telomere length, which were significantly associated with OS in univariate analysis. Along with age (P=0.003), Binet C (P<0.001), ECOG status (P=0.017), s-TK (P=0.009), IGHV (P=0.001) and presence of 17p- and/or TP53 mutation (P=0.003), telomere length (HR 1.479; 95%CI 1.064-2.058; P=0.020) was also identified to be an independent prognostic factor for OS in the CLL11 cohort.
In summary, short telomere length in CLL was found to be associated with other adverse biological disease characteristics as well as treatment efficacy, as an independent prognostic factor for PFS and OS in the context of CLB based therapy. The study suggests the value to assess telomere length for risk stratification of CLL patients and to evaluate this marker in the context of novel treatment options targeting biological disease features.
Bahlo: F. Hoffmann-LaRoche: Honoraria, Other: travel grants. Goede: Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ritgen: BMS: Consultancy, Other: travel support; F. Hoffmann-LaRoche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding; Gilead: Other: travel support; Pfizer: Consultancy. Fingerle-Rowson: F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Employment. Kneba: AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-LaRoche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding; Janssen-Cilag: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding. Fischer: Roche: Other: Travel Grants. Hallek: AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-LaRoche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen-Cilag: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Stilgenbauer: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Hoffman La-Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal